Want to learn SEO in 2026 but don’t know where to start?
This step-by-step SEO tutorial for beginners will teach you exactly how search engine optimization works, in simple words, without technical jargon.
Whether you run a blog, business website, or online store, SEO helps you get FREE traffic from Google by making your pages easier to find and rank.
The good news? You don’t need years of experience or expensive tools to start learning SEO.
We’ve relied on these same SEO principles for years to gain millions of search visitors, and today, this blog earns over $18,000 per month thanks to SEO.
These SEO basics work not just for established sites like BloggersPassion but also for newer projects.
For example, after acquiring WPCoupons.io last year, we applied these same fundamentals, and with a few tweaks, the site grew to 10,000 visits in 2025, proof that the basics truly work.
In this beginner-friendly guide, you’ll learn:
- What SEO is and how search engines work
- The basics of on-page, technical, and off-page SEO
- How to find profitable keywords?
- How to create content that ranks on Google
- Simple strategies to track and improve your SEO results
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll understand the exact process beginners use to start ranking on Google and how to apply it to your own website.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
- What Is SEO? A Simple Explanation for Beginners
- How Search Engines Work?
- Types of SEO Explained: Technical, On-Page, and Off-Page SEO
- Technical SEO Basics for Beginners (Simple Checklist)
- On-Page SEO Explained
- Off-Page SEO Explained
- The SEO Process: What Actually Works
- Final Thoughts On SEO Tutorial 2026 For Beginners
- FAQs About SEO guide for beginners
What Is SEO? A Simple Explanation for Beginners
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the process of improving your website’s content, structure, and visibility so that it appears HIGHER in search engines when people search for topics related to your content or business.
In simple terms, SEO helps people find your website without paying for ads.
Why SEO Is Important for Websites?
Most people click one of the first results they see on Google.
If your website doesn’t show up on page #1, people may never find it.
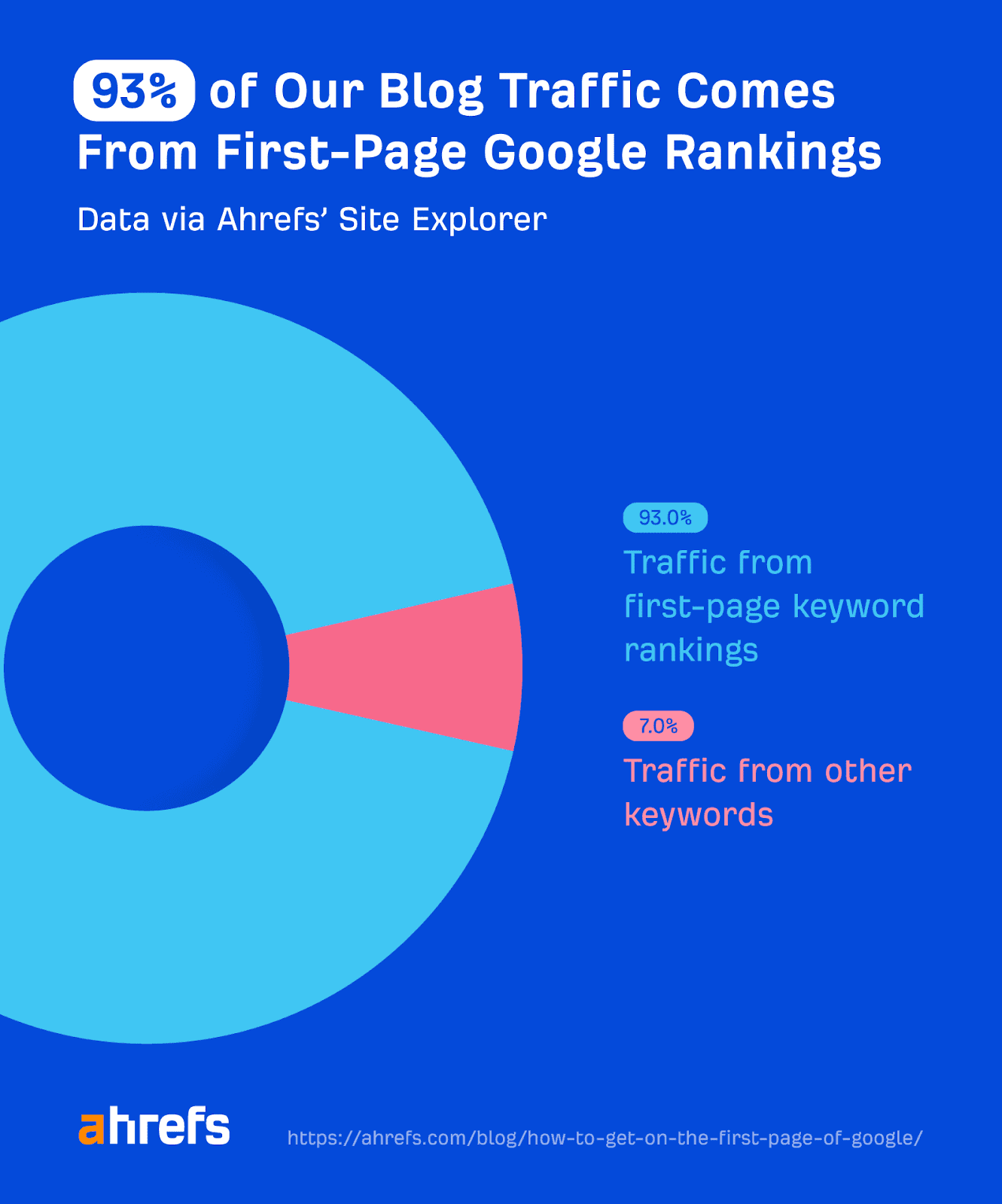
It’s how authoritative websites like Ahrefs get almost all their traffic from first-page Google rankings.
SEO helps you:
- Get free traffic from search engines
- Reach people already searching for your topic
- Build trust and credibility
No matter how good your products or content are, they may never be discovered without proper SEO.
Organic Traffic vs Paid Traffic
- Organic Traffic (or SEO): Visitors who find your website through free search results on Google
- Paid Traffic (Or PPC): Visitors who come from ads you pay for (Google Ads, social ads, etc.)
SEO focuses on organic traffic, which is free, while paid traffic stops when you stop paying for ads.
How Search Engines Work?
Search engines store large numbers of web pages (sometimes billions) in their indexes.
When you search for something, search engines quickly scan those pages and show the ones that best match your query.
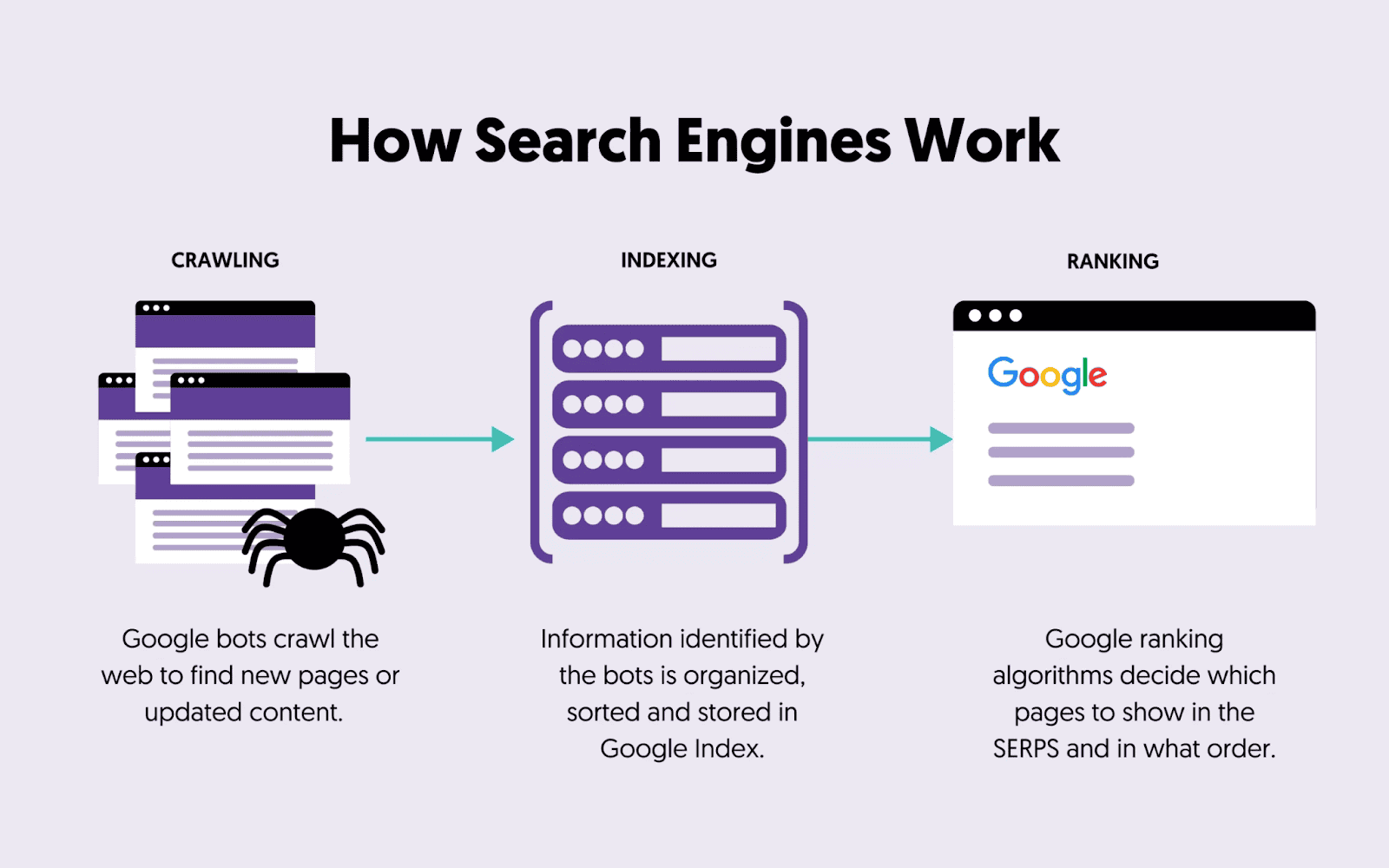
Search engines work through three steps:
- Crawling
- Indexing and
- Ranking
Let’s briefly discuss them.
What Is Crawling in SEO?
Crawling is when Google sends its bots (called spiders or Googlebot) to scan the entire internet and find newly updated content.
What Is Indexing in Google Search?
After crawling a page, Google tries to understand what the page is all about and stores it in its database. This is called indexing.
Google analyzes everything from the text to images and video files on the page.
How Google Ranks Websites in Search Results?
Google considers over 200 factors to rank web pages, such as:
- Content quality and relevance
- Use of keywords strategically
- Technical SEO
- Backlinks from other websites
- User Experience (UX)
Websites that perform better in these areas usually rank higher.
Why Some Pages Don’t Rank on Google?
A page may not rank well if:
- Google hasn’t crawled or indexed it yet (#1 reason)
- The content is thin, duplicate, or not useful
- The page doesn’t match the search intent
- The website is slow or hard to use
- There are few or no backlinks
Improving these factors helps your page move up in search results. Now, let’s dive into the foundation.
Types of SEO Explained: Technical, On-Page, and Off-Page SEO
SEO is usually divided into three main types. Each one helps your website rank better in a different way.
- Technical SEO
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on improving your website to make it easier for search engines to crawl, understand, and access your content.
It includes things like:
- Fast page loading times
- Mobile-friendly design
- Fixing broken links
- Creating a sitemap for Google
- Perform regular site audits
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is about improving the content and elements on your web pages.
The most important part is matching the search intent.
It includes:
- Writing helpful content
- Optimizing titles and headings
- Adding internal links
- Using images and visuals
- Using proper formatting for better readability
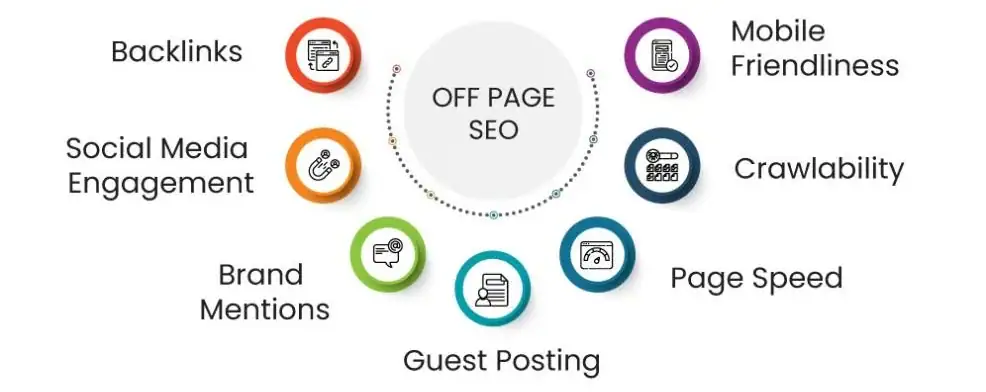
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to efforts outside your website that help increase its authority and trust.
The most important part is getting backlinks from other websites to your website.
It includes:
- Guest posting
- Brand mentions
- Social media sharing
- Influencer marketing
Technical SEO Basics for Beginners (Simple Checklist)
- Add basic schema markup (structured data) for better search visibility
- Make sure Google can crawl and index your site
- Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console
- Make your site fully mobile-friendly
- Improve page speed and Core Web Vitals
- Fix broken links and server errors
- Keep your site structure simple and easy to navigate
- Add internal links between related pages
- Remove duplicate content
- Make sure every page has a proper SEO title and meta description
On-Page SEO Explained
On-page SEO involves optimizing a page’s content and HTML source code, as well as improving your site’s user-friendliness.
Simply put, it takes care of everything you can do on your website, such as page titles, internal linking, meta tags & descriptions. On-page SEO consists of the elements of SEO you can control most effectively.
Have a look at the following illustration to see the various factors involved in a website’s SEO.

However, there are three main things you should focus on if you are serious about improving your search traffic in 2026, as listed below.
1. Write Content That Google Loves
People visit your site only when your content helps them solve a problem or answer a question. If your page gives the most HELPFUL answer, Google is more likely to rank it higher.
Example: If someone searches “how to lose belly fat at home,” a short 300-word article saying “eat healthy and exercise” won’t rank.
A guide with workouts, a simple meal plan, tips, and FAQs has a much better chance.
What makes your content rank-worthy?
- Pick a clear topic and a primary keyword first. Decide what people are searching for before you start writing.
- Once you start writing, make sure you include all the statistics and helpful information in your content.
- Without keyword research, even great content fails. Include your targeted keyword in your post’s headline and throughout the article. Choose your keyword before starting to write.
- Answer the question clearly. This is important, as you need to provide a direct, simple answer so Google can recognize your page as useful for that search.
- Google loves fresh content, so publish new articles or update existing ones with more up-to-date information.
- If you write a clear-cut answer, then Google recognizes it as an answer to a particular question.
2. Optimize Your Content the RIGHT Way
Even the best content won’t rank if it isn’t properly optimized for search and user intent. Here are some best practices to optimize content.
Match search intent first: Make sure your page answers exactly what the user is looking for (guide, comparison, steps, product, etc.). Analyze the top 5 ranking articles around your topic to analyze the search intent.
Cover the topic in depth: Add examples, FAQs, steps, visuals, and related questions so the page feels complete and useful.
Use your primary keyword in the title: Keep titles around 50–60 characters. Make them clear, clickable, and include the main keyword naturally.
Write a strong meta description: Include the main keyword once, keep it to 135–160 characters, and add a small CTA such as Learn more, Read guide, or See tips. Focus on improving clicks, not stuffing keywords.
Mention your keyword in the introduction: Use the primary keyword once in the first paragraph naturally. Focus on explaining what the article will help the reader achieve.
Optimize your URL: Keep URLs short, readable, and meaningful. Add the keyword if it fits naturally. Avoid long numbers or random words.
Use proper headings (H1, H2, H3): H1 for the title, H2 for main sections, H3 for sub-sections. Clear headings help both readers and Google understand your content. Add keywords only when natural.
Add structured data (schema markup): Use FAQ, HowTo, Review, or Article schema to increase chances of rich results in Google. Use plugins like RankMath to implement schema without touching code.
Add descriptive image alt text: Explain what the image shows in simple words. This improves accessibility and helps images appear in search. Use keywords only if relevant.
Use internal links wisely: Link to related posts or pages that genuinely help the reader. This improves navigation, keeps users longer, and improves overall site structure.
3. Improve User Experience with Smart Site Structure
Google ranks sites that are easy to use, fast, and simple to navigate. Good structure helps both users and search engines understand your site.
What to optimize?
- Make pages easy to crawl: Use clear menus, internal links, and no broken links. Google should be able to reach any page in a few clicks.
- Use a simple site hierarchy: Group related posts into categories and link them together (topic clusters).
- Fix duplicate content properly: If the same page appears at two URLs, use a canonical tag or a301 redirect to the main page. Don’t leave duplicates live.
- Make your site mobile-first: Most users come from phones. Use readable text, clickable buttons, and no horizontal scrolling.
- Improve page speed: Compress images, use a fast hosting provider, and reduce the number of heavy plugins/scripts. Aim for a load time under ~3 seconds.
- Add clear internal navigation: Use breadcrumbs, related posts, and contextual links so users don’t get lost.
- Avoid orphan pages: Every important page should have at least one internal link pointing to it.
Off-Page SEO Explained
Off-page SEO focuses on increasing your website’s authority through backlinks, social signals, brand mentions, and user engagement.
If you’re serious about growing traffic, pay attention to these three off-page SEO factors that improve your site’s authority, trust, and visibility across the web.
1. Build Trust With Strong Off-Page SEO Signals
To rank in Google’s top results, your website MUST look trustworthy and authoritative. Google checks E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust).
That’s why websites with strong reputation, mentions, and backlinks usually rank higher than new sites with no external signals.
Here’s how to build trust using off-page SEO:
- Increase authority: Get backlinks from respected websites in your niche. The more high-quality sites mention or link to you, the stronger your domain and page authority become.
- Domain age matters: If you haven’t got your site up and running yet, then find an affordable, expired domain and start using it.
- Build your brand identity online: Build a strong network through blogging, boost your social media presence, and get mentions on other websites. When Google sees your name or brand across the web, it increases trust.
2. Get Backlinks From Trusted Websites
Backlinks are links from other websites to yours. They act like trust signals — the more relevant, strong links you earn, the easier it is to rank higher in Google.
But quality beats quantity. A few links from trusted sites help more than hundreds of spammy ones.
Example: A fitness blog getting a link from Healthline or a well-known health-related site = strong signal.
Getting 200 links from random low-quality directories = little or no benefit.
Well, now the question is: how do you get links from authority sites?

Guest post on relevant sites: Write a useful article for another blog in your niche and include a link to your site.
Create link-worthy content: publish original research, tools, checklists, or in-depth guides that people naturally reference.
Find competitor backlinks: Use SEO tools like Semrush to see who links to your competitors, then pitch your better or updated content to those same sites.
Replace broken links: Find a page that links to a dead resource and suggest a similar article instead. Example: If a blog links to a deleted “Protein Diet Plan,” offer your updated version.
Add expert quotes or interviews: Feature influencers or experts in your article. Many will share or link to it.
Update or improve existing content elsewhere: Offer site owners a fresher stat, a new section, or a better guide, as they may credit you with a link.
Use visuals that people reuse: Create infographics, charts, or stat images that other sites embed with credit. Example: A simple chart showing “Calories burned in 10 common workouts.”
Backlinks remain the most powerful off-page ranking signal. Did you know that top-ranking pages have more backlinks than lower-ranking pages?
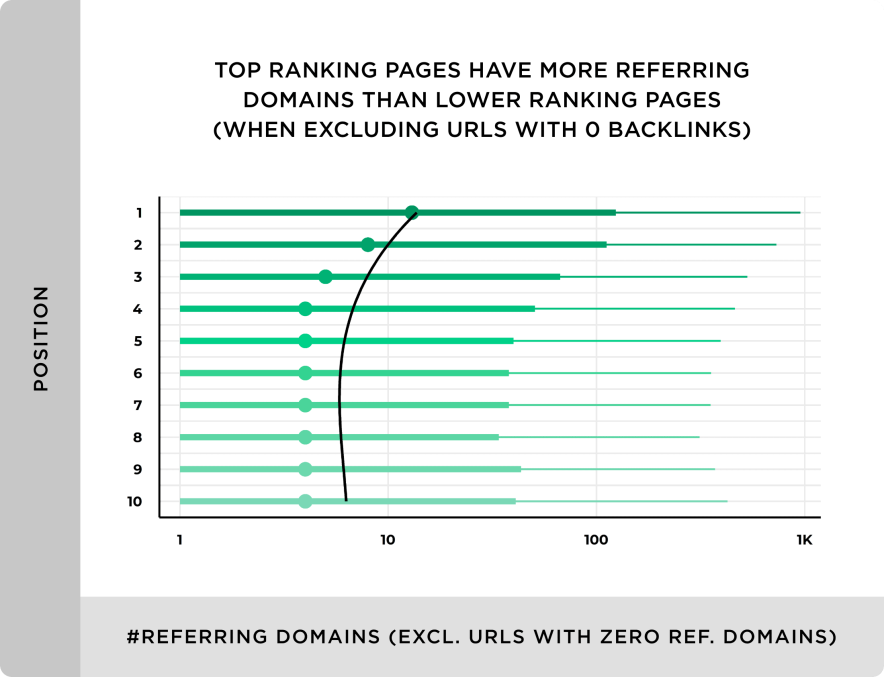
High-quality backlinks
Focus on earning links from relevant and trusted websites in your niche.
One strong link from an authority site is far more valuable than dozens of low-quality links. Use natural anchor text and prioritize quality over quantity as you steadily scale your website’s backlink profile.
Stay active on social platforms
Social media boosts your visibility and helps your content reach the right audience.
When influencers or niche communities share your content, it increases exposure, brand searches, and chances of earning backlinks, all of which improve off-page SEO signals.
Engage in communities and Q&A platforms
Participate in niche forums and social networking sites like Reddit and Quora by answering questions and sharing helpful advice.
Add links to your content only when they genuinely help the reader. Consistent participation builds authority, relationships, and targeted referral traffic over time.
The SEO Process: What Actually Works
The key steps that actually drive SEO results: start by finding profitable keywords your audience is searching for, then create optimized content around them. After publishing, track rankings, traffic, and user behavior regularly to see what’s working and improve over time. Let’s briefly discuss these steps now.
Build A List Of Profitable Keywords
To grow your blog traffic, start by finding the right keywords, terms people actively search for, and that match your content or offer.
Once you build a solid list of all profitable keywords, you can plan and publish content around those topics consistently.
Before building the list, you need to understand long-tail keywords.
If you ignore long-tail keywords, you miss highly targeted traffic. These searches are more specific, less competitive, and usually convert better because users already know what they want.
For example:
- Short-tail: “protein powder”
- Long-tail: “best protein powder for weight loss in 2026”
What are long tail keywords?
Long tail keywords are four or more keywords that are more specific and get less search traffic but will usually have a higher conversion value.
Here’s a quick illustration showing the difference between short-tail and long-tail keywords.

Here are the tools that will help you can find long-tail keywords for your niche:
- Google Autocomplete: Start typing your topic in Google search and note the suggested keyword phrases; these are real long-tail searches people use.
- Ubersuggest: This tool provides all the keywords and data you need to make informed decisions. It also provides you with keywords that are not available through the Google Keyword Planner.
- Soovle: This free keyword research tool provides autocomplete suggestions from a variety of sources to help you boost your search volume.
Instead of writing about 10 different topics, focus deeply on one main topic and cover it from every angle. When your site has multiple helpful pages on the same subject, Google sees you as an expert and ranks you higher.
Example: If your topic is weight loss, don’t stop at one post. Create supporting blog posts like:
- Beginner weight loss diet plan in New York
- Best high-protein foods for fat loss
- Home workout plan for beginners
- How many calories to lose 5 pounds safely
Link these articles to each other and keep updating them.
Track Your SEO Progress
After working on on-page SEO, backlinks, and other off-page efforts, start tracking your results to see what’s improving and what needs fixing.
The Importance Of SEO Tools
SEO is complex, and the right tools make it easier to measure performance and find opportunities. While many tools exist, only a few provide reliable data. Here are some I recommend for beginners.
Rank Math SEO: It’s free and easy to use. If you want to boost your on-page SEO, this plugin is a must-have.
Semrush: We’ve used this SEO tool for 10+ years — it helped me triple my search traffic and boost website sales. It’s a must-have for anyone serious about rankings and growth.
Google Analytics: Wanna learn more about your visitors? Then monitor your organic search traffic sources to see what keywords people are using to find your website in search results. So you will understand which keywords to target with your SEO campaign.
Final Thoughts On SEO Tutorial 2026 For Beginners
SEO isn’t hard — it gets simple once you understand the basics.
If you’re just starting, focus on one area at a time — whether it’s on-page SEO, site audits, or link building and grow from there. The best way to learn SEO is to start your own blog.
What do you think of this tutorial? Have any SEO tips to add? Share your thoughts in the comments.
FAQs About SEO guide for beginners
Here are a few important questions about the SEO guide for beginners.
Start your own blog or site and practice keyword research, content writing, and optimization. You can also follow the top SEO blogs such as Semrush, Ahrefs, Backlinko, etc to learn SEO from scratch.
Yes. Beginners can learn SEO by understanding basics like keyword research, on-page optimization, site audits, and link building.
The three most important types are on-page SEO (optimizing content and site elements), off-page SEO (building backlinks and online authority) and technical SEO (site audits, crawling, etc)
Popular beginner tools include Semrush, Ahrefs, Ubersuggest, Moz, RankMath, and SpyFu for research, optimization, and tracking.
Robots.txt is a file that tells search engines which pages on your website to crawl and index, and which to ignore.
SEO is best for long-term free traffic, while PPC is ideal for quick, paid results. The right choice depends on your goals and timeline.
Track metrics like keyword rankings, organic traffic, CTR, bounce rate, backlinks, domain authority, mobile traffic, and time on page.




Hi Anil Bro,
Since SEO is quite difficult after Google Algorithm updates but I think the tips you have mentioned in this article will help bloggers to rank their site in SERP. But Really Anil Bro you have Mentioned Great Knowledge about Off page SEO and ON Page SEO.
Thanks Anil, so detailed and fascinating! It’s really good tips for on page and off page SEO. The recommended links are awesome too and got the several meaningful information from there.
Great post i follow both seo – onPage seo and offpage seo buy my traffic drop dramatically. Can you me ideas how to fix them?
Hey Anil Really superb post.
The SEO is the backbone of any website as it drives organic traffic from search engines. The tips and tricks you explained in this article is superb and sure I will try out in my website.
There is always some updates from google about its algorithm and it bit difficult to track all. Your opinion on this if any. Thanks in advance
Hey Anil great post.
Just a question you mentioned that one should build quality backlinks at scale for your website. Do you mean building do-follow links or on the websites having high trust rank.
And do social shares of a page have any weigh on the google search ranking for that page.
This is a great tutorial. I learned a few new things. Also thanks for including links to some of the tools that are out there. I look forward to reading more articles you write.
This is epic post bro. Very insightful to all newbies out there. Each and every blogger should speak, eat, sleep and breathe SEO. People forget on page SEO and start chasing Off page SEO tactics. On-page SEO is equally important. I would suggest people research on topics before writing any article. Semrush + Buzzsumo are the ideal combinations for keyword and content research.
Hi Rupesh, glad you liked this SEO tutorial for beginners. That’s a great quote, but you don’t have to take SEO so much seriously especially when you’re starting out. Instead, look for ways to add value to people with your content. Yes, on page SEO important if you want to get better rankings for your target keywords.
As I’m a beginner in SEO the things which you mention here is really awesome for SEO guys. Can anyone tell me I m only know Off page SEO how can I do on page SEO or have you any tutorials for on page SEO. Please give me.
If you’re looking for on page and off page SEO tips at one place, I recommend you to check out this post: https://bloggerspassion.com/seo-tutorial-for-beginners/ where you can learn everything about SEO in 1 or 2 hours, must read guide for beginners, Alok.
Very good post. Both on page and off page SEO are necessary for a website. I am working on page SEO now.
This post is great for beginners as well as some professionals.
Hi Saurabh, yes, both on page and off page SEO are necessary for a website to rank well in search engines. Just make sure to take small steps instead of focusing on too many things at once. I recommend you to check out this post: https://bloggerspassion.com/seo-tutorial-for-beginners/ if you want more info about best SEO tips.
Hello Anil,
Great Post. SEO is considered as backbone of your site traffic. It will help you to drive huge organic traffic free of cost. By implementing the right SEO strategies anyone can rank their site. Since SEO is quite difficult after Google Algorithm updates but I think the tips you have mentioned in this article will help bloggers to rank their site in SERP.
Hi Vishwajeet, yes SEO is hard because Google makes a ton of changes every year. Just focus on timeless SEO related stuff such as creating great content, attracting quality links and so on and you’ll get long lasting results.